Electron Transport Chain | Class 11 | ETC | FBISE | NBF
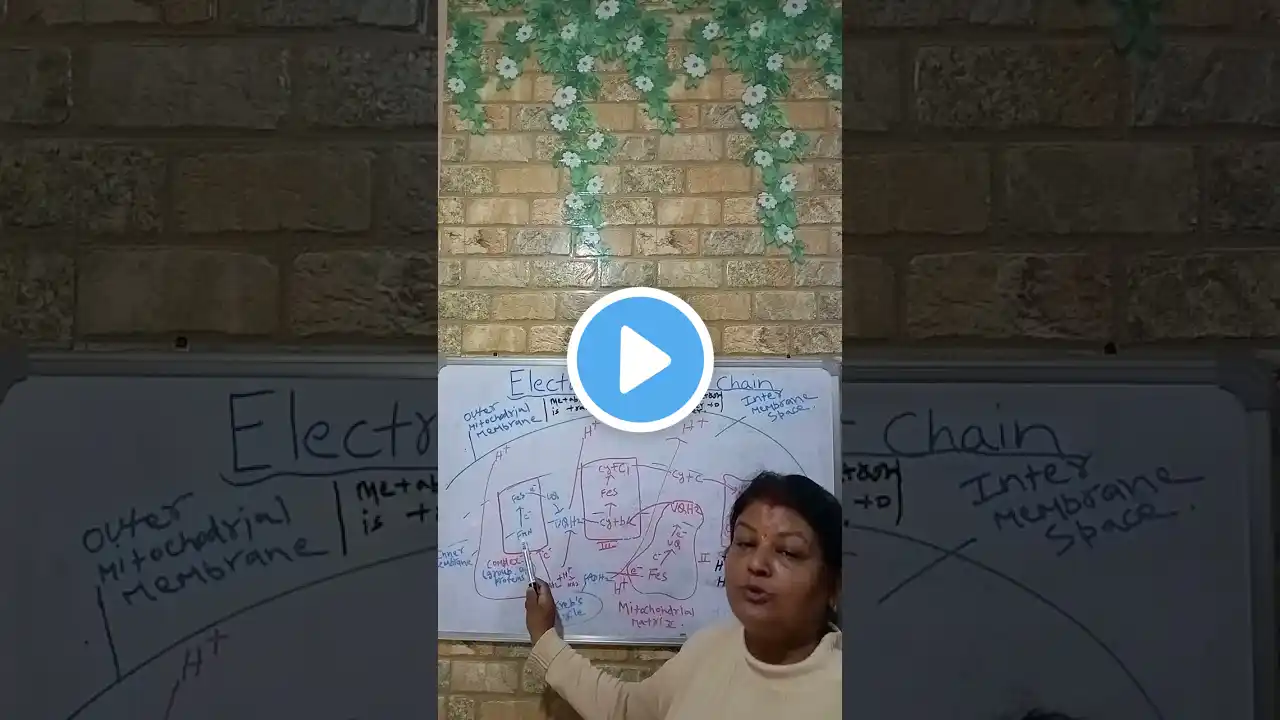
The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes located in the mitochondrial inner membrane, responsible for generating energy for the cell through the process of cellular respiration. Here's a step-by-step description: 1. *Electron transfer*: Electrons from NADH and FADH2 (generated in the citric acid cycle and fatty acid oxidation) are passed through a series of electron carriers in the ETC. 2. *Proton pumping*: As electrons flow through the ETC, protons (hydrogen ions) are pumped across the mitochondrial inner membrane, creating a proton gradient. 3. *Proton gradient*: The proton gradient generates a pH gradient and an electric potential across the membrane. 4. *ATP synthesis*: The energy from the proton gradient is used to drive the production of ATP through the process of chemiosmosis. 5. *Complexes*: The ETC consists of four complexes: Complex I (N #electrontransportchain #etc #federalboard #biology #onlinebiology #bioclass #science #onlinelearning #science #onlinebiologytutorials #class11 #class12 #kpkboard