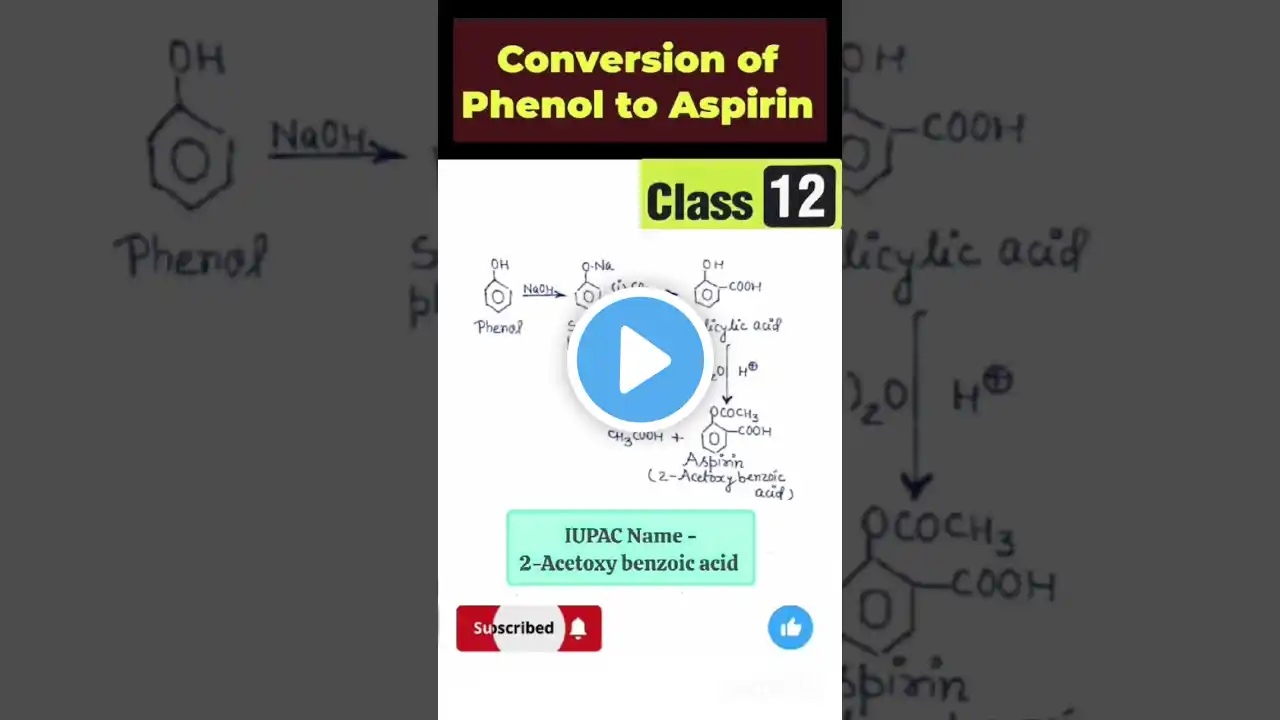
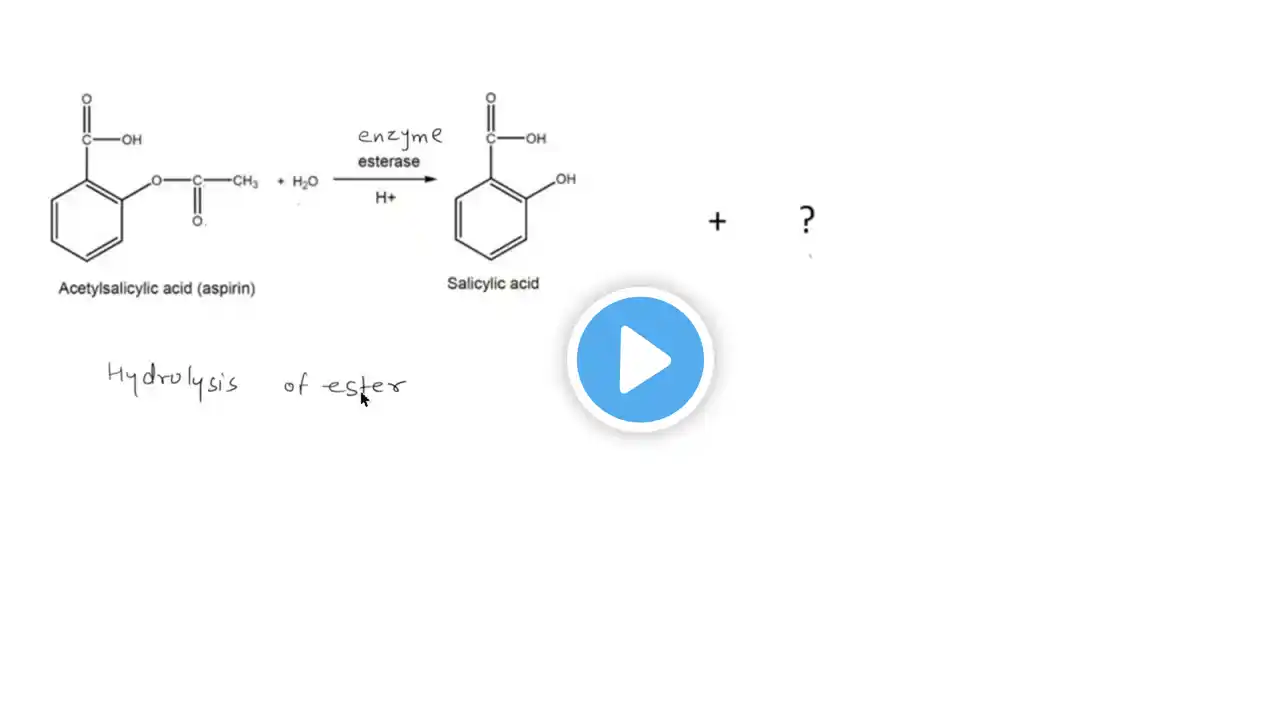
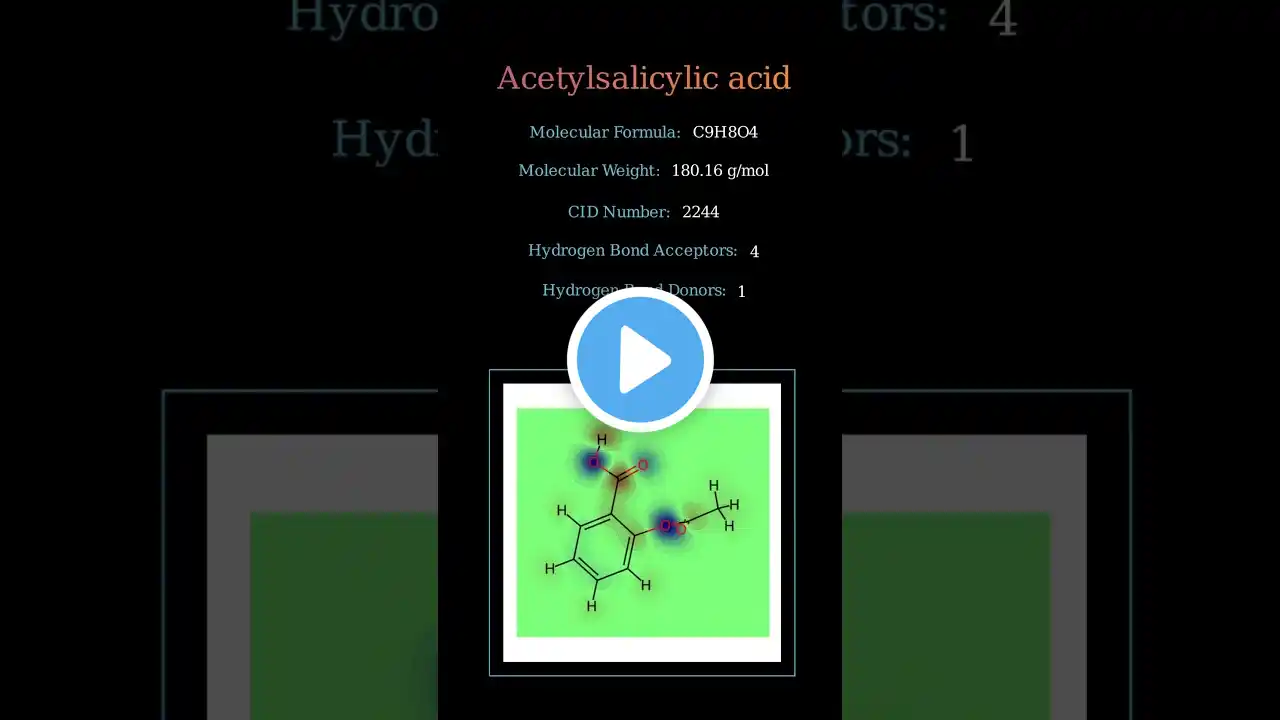
Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid)
Now that we understand the basics regarding NSAIDs, let's dive into a few specific drugs from this class. First up, aspirin. This drug has been around for centuries, but now with a modern understanding of chemistry and biochemistry, we are able to understand its precise structure and mechanism of action. Aspirin is unique among NSAIDs because it covalently alters a serine residue in the active site of cyclooxygenase enzymes, thereby rendering the enzyme permanently incapable of producing prostaglandins. This is what leads to aspirin's anti-inflammatory effects. Let's get a closer look at this activity now. Script by Chris Hofmann Watch the whole Pharmacology playlist: http://bit.ly/ProfDavePharma General Chemistry Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveGenChem Organic Chemistry Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveOrgChem Biochemistry Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveBiochem Biology/Genetics Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveBio Anatomy & Physiology Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveAnatPhys Biopsychology Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveBiopsych Microbiology/Infectious Diseases Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveMicrobio History of Drugs Videos: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveHistoryDrugs Immunology Tutorials: http://bit.ly/ProfDaveImmuno EMAIL► [email protected] PATREON► / professordaveexplains Check out "Is This Wi-Fi Organic?", my book on disarming pseudoscience! Amazon: https://amzn.to/2HtNpVH Bookshop: https://bit.ly/39cKADM Barnes and Noble: https://bit.ly/3pUjmrn Book Depository: http://bit.ly/3aOVDlT