AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM || MCQS | PHARMACOLOGY
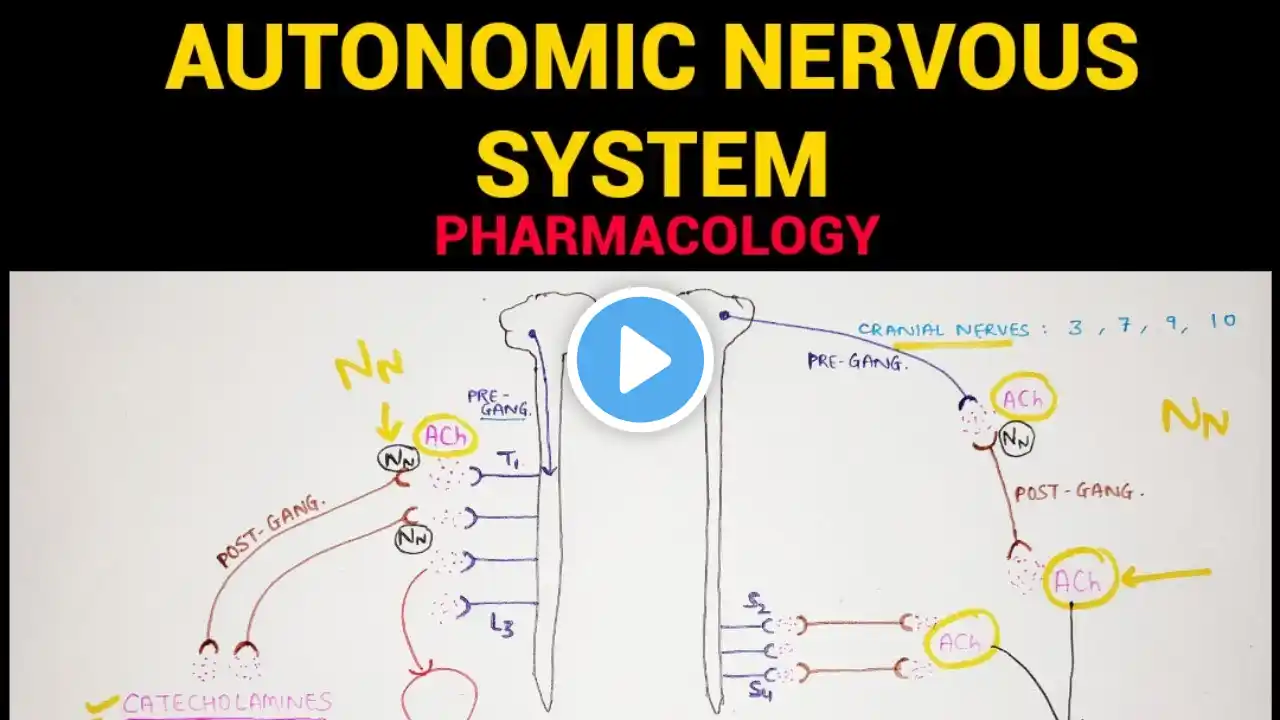
Drugs acting on ANS MCQs pharmacology part-2 Autonomic nervous system (A.N.S.) is a peripheral complex of nerves, plexuses and ganglia that are organized to modulate the involuntary activity of the secretory glands, smooth muscles and visceral organs. This system functions to sustain homeostatic conditions during periods of reduced physical and emotional activity, and equally important, to assist in internal bodily reactions to stressful circumstances. Nerves transmit their impulses across most synapses and neuroeffector junctions by means of specific chemicals called as neurohumoural transmitters or simply neurotransmitters. The autonomic drugs exert their actions on smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, glands and visceral organs by mimicking or modifying the action of neurotransmitters released by autonomic fibres either at ganglia or at effector cells. In this video and its affiliated parts in the peripheral nervous system section, multiple-choice questions about drugs acting on autonomic nervous system in terms of uses, common side effects, mechanism of action, drug interactions, contraindications, and many important questions that you may encounter in many exams. MCQs: 1. The reversible cholinesterase inhibitor indicated in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease is a Pyridostigmine b. Edrophonium c. Neostigmine d. Tacrine e. Ambenonium 2. Ritodrine hydrochloride is used in the treatment of a. Parkinson's disease b. Bronchial asthma c. Depression d. Hypertension e. Premature labor 3. Hypotension, bradycardia, respiratory depression, and muscle weakness, all unresponsive to atropine and neostigmine, would most likely be due to a. Diazoxide b. Isoflurophate c. Nicotine d. Tubocurarine e. Pilocarpine 4. The skeletal muscle relaxant that acts directly on the contrac" mechanism of the muscle fibers is a. Gallamine b. Dantrolene c. Pancuronium d. Cyclobenzaprine e. Baclofen 5. The cholinomimetic drug that is useful for treating postoperative abdominal distention and gastric atony is a. Acetylcholine (ACh) b. Methacholine c. Carbachol d. Bethanechol e. Pilocarpine 6. Neostigmine will effectively antagonize skeletal muscle relaxation produced by a. Pancuronium b. Succinylcholine c. Diazepam d. Baclofen e. Nicotine 7. The skeletal muscles that are most sensitive to the action of tubocurarine are the a. Muscles of the trunk b. Muscles of the arms and legs c. Respiratory muscles d. Muscles of the head, neck, and face e. Abdominal muscles 8. Both phentolamine and prazosin a. Enhance gastric acid secretion through a histamine-like effect b. Have potent direct vasodilator actions on vascular smooth muscle c. Are competitive antagonists at adrenergic receptors d. Cause hypotension and bradycardia e. Are used chronically for the treatment of primary hypotension 9. Of the following structures, which does not respond to beta-adrenergic receptor stimulation? a. Ciliary muscle of the iris b. Radial muscle of the iris c. Bronchial muscle d. Atrioventricular (AV) node e. Sinoatrial (SA) node 10. A l6-year-old male treated for bronchial asthma develops skeletal muscle tremors. Which of the following agents may be responsible for this finding? a. Ipratropium b. Zileuton c. Beclomethasone d. Cromolyn e. Salmeterol 11. Of the following, which will not be blocked by atropine and scopolamine a. Bradycardia b. Salivary secretion c. Bronchoconstriction d. Skeletal muscle contraction e. Miosis 12. Which of the following agents should a patient take for a stuffy, runny nose? a. Oxymetazoline b. Albuterol c. Clonidine d. Terbutaline e. Metoprolol 13. A 65-year-old male has a blood pressure of 170/105 mmHg. Which of the following would be effective in lowering this patient's blood pressure a. Methylphenidate b. Terbutaline c. Dobutamine d. Pancuronium e. Prazosin 14. Nicotine in low doses may cause a. Decreased tone and motor activity of the small intestine b. Stimulation of the respiratory rate and depth c. Miosis d. Bradycardia 15. Which of the following agents might mask the hypoglycemia in treated diabetics? a. An alpha-adrenergic agonist b. An alpha-adrenergic antagonist c. A beta-adrenergic agonist d. A beta-adrenergic antagonist e. A cholinergic agonist Music by https://hypeddit.com/track/t2axt6 Provided by: https://bit.ly/YouTubeEMW • NO COPYRIGHT Upbeat Background Music ... videos links Prometric exam DHA and SLE • #prometric #SLE and #DHA mcqs pharmac... Pharmacy sig codes • prescriptions #abbreviations || sig ... Antidote and anti poisoning agent • Antidotes || poisoning indication || ... Biochemistry: • Biochemistry (carbohydrates) mcqs part 1 MCQs of drugs used in disorders of coagulation part-1 • Drugs used in disorders of coagulatio... MCQs of drugs acting on hematopoietic system part-1 • Drugs Acting On Hematopoietic System ... MCQs of anxiolytics agents part-1 • Anxiolytic agents | Anti-anxiety | Be... MCQs of pharmacology very important questions part-6 • Pharmacology MCQs part-6 || Very impo... • Antiparkinsonian drugs mcqs | pharmac... NAPLEX pass rate MCQs part-1 • mcqs of pharmacology and medicinal ch... #mcq #ANS #shorts