SEED GERMINATION + TYPES OF GERMINATION and Conditions for Germination 10th Class
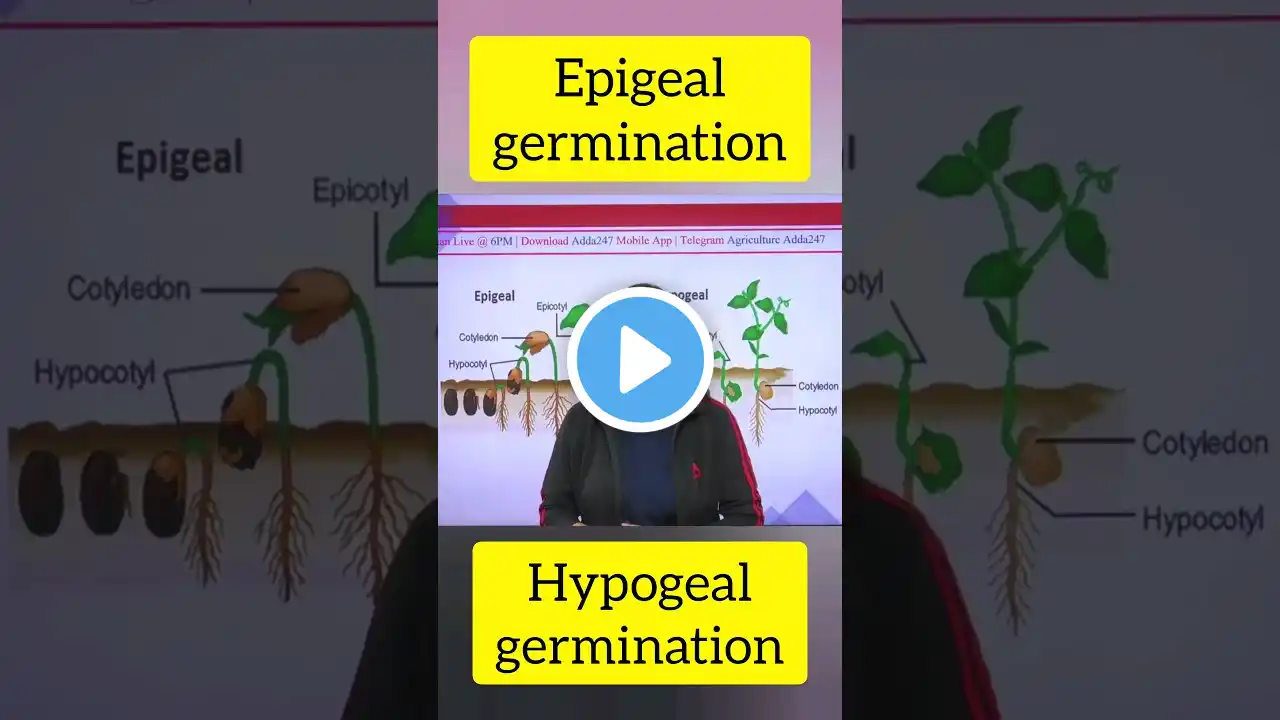
#Seed germination is the process where a seed develops into a seedling under favorable conditions, requiring water, oxygen, and appropriate temperature, and sometimes light. There are two main types: epigeal (cotyledons above ground) and hypogeal (cotyledons below ground). Here's a more detailed explanation: What is Seed Germination? It's the initiation and continuation of growth of a seed, leading to the emergence of a seedling. Seeds remain dormant until conditions are right for germination. The process involves the seed absorbing water, activating enzymes, and initiating metabolic processes. Types of Germination: Epigeal Germination: The cotyledons (seed leaves) are carried above the soil surface by the elongation of the hypocotyl (stem below the cotyledons). Hypogeal Germination: The cotyledons remain below the soil surface, with the hypocotyl elongating but not carrying the cotyledons above ground. Conditions for Germination: Water: Seeds need water to absorb and swell, which is crucial for activating enzymes and initiating growth. Oxygen: Germinating seeds need oxygen for respiration to provide energy for growth. Temperature: Optimal temperature ranges vary depending on the seed type, but most seeds require a moderate temperature range (e.g., 25-30°C). Light: Some seeds require light for germination, while others germinate in darkness or are indifferent to light. Other Factors: Soil Conditions: A well-drained, fine-textured seedbed with good seed-to-soil contact is important. Nutrients: While not directly involved in germination, the availability of nutrients in the soil is essential for seedling growth. #biology #education #the #cellbiology