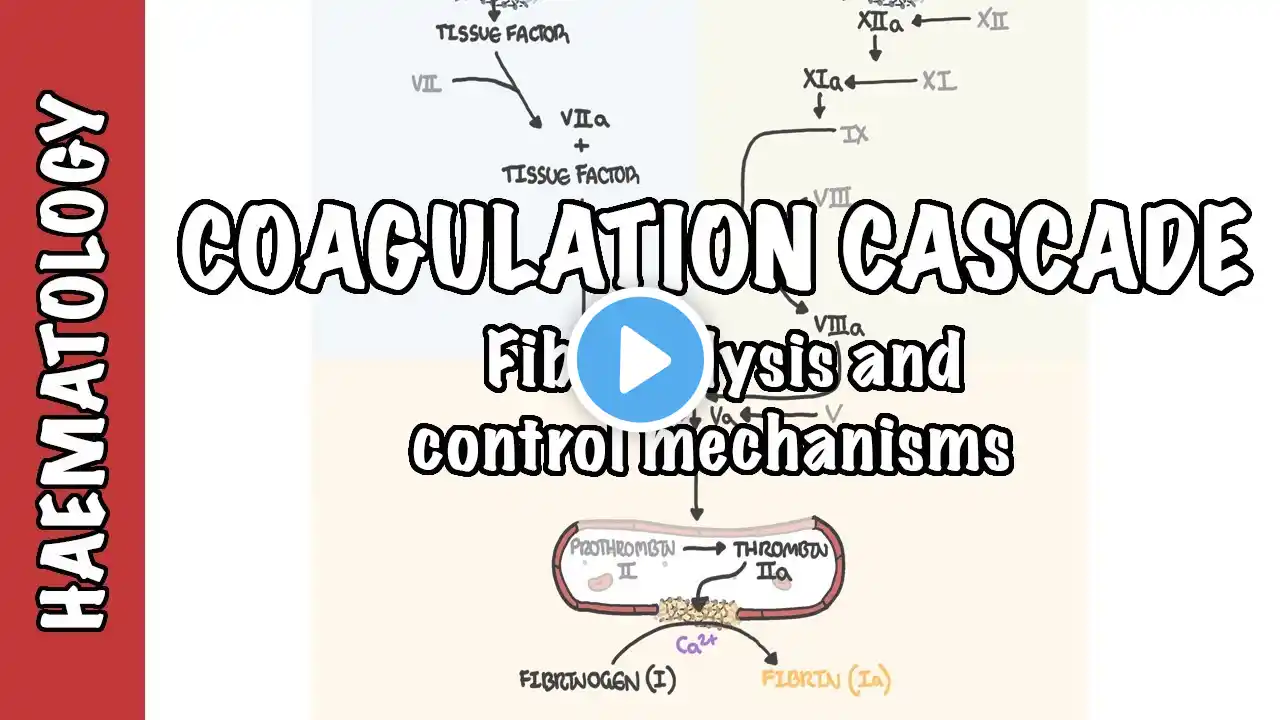
Extrinsic and Intrinsic Blood Coagulation Pathway and their Negative Feedback Inhibitors
Blood Coagulation Pathways The process of blood coagulation involves a complex cascade of events that can be divided into two main pathways: the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. These pathways converge at a common point, leading to the formation of a blood clot. Intrinsic Pathway Initiation: Triggered by damage to the blood vessel's inner lining (endothelium) and exposure of collagen. Key Factors: Factor XII (Hageman factor) is activated, which then activates Factor XI. Factor XI activates Factor IX in the presence of calcium ions (Ca²⁺). Factor VIII and Factor IXa activate Factor X. Activation: The intrinsic pathway primarily involves factors that are already present within the blood. Progression: Factor X is activated to Factor Xa, which combines with Factor V, Ca²⁺, and phospholipids to form the prothrombinase complex. Negative Feedback Inhibitors: Antithrombin III (AT III): Inhibits activated factors, particularly thrombin (Factor IIa), Factor IXa, and Factor Xa. Protein C and Protein S: Activated protein C, with its cofactor protein S, inactivates Factors Va and VIIIa. Extrinsic Pathway Initiation: Triggered by external trauma that exposes tissue factor (TF), also known as Factor III. Key Factors: Tissue factor binds with Factor VII, which is then activated to Factor VIIa. Activation: The extrinsic pathway primarily involves factors that are external to the blood. Progression: The TF-Factor VIIa complex activates Factor X, which then follows the same pathway as the intrinsic pathway to form the prothrombinase complex. Negative Feedback Inhibitors: Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI): Inhibits the TF-Factor VIIa complex and Factor Xa. Common Pathway Once Factor X is activated (either by the intrinsic or extrinsic pathway), it leads to the conversion of prothrombin (Factor II) to thrombin (Factor IIa). Thrombin then converts fibrinogen (Factor I) to fibrin, forming a stable blood clot. Summary of Negative Feedback Inhibitors Antithrombin III (AT III): Inhibits thrombin, Factor IXa, and Factor Xa. Protein C and Protein S: Inactivate Factors Va and VIIIa. Tissue Factor Pathway Inhibitor (TFPI): Inhibits the TF-Factor VIIa complex and Factor Xa. #BloodCoagulation