Menstrual Cycle Phases | Female Reproductive System | Follicular Luteal Proliferative Secretory
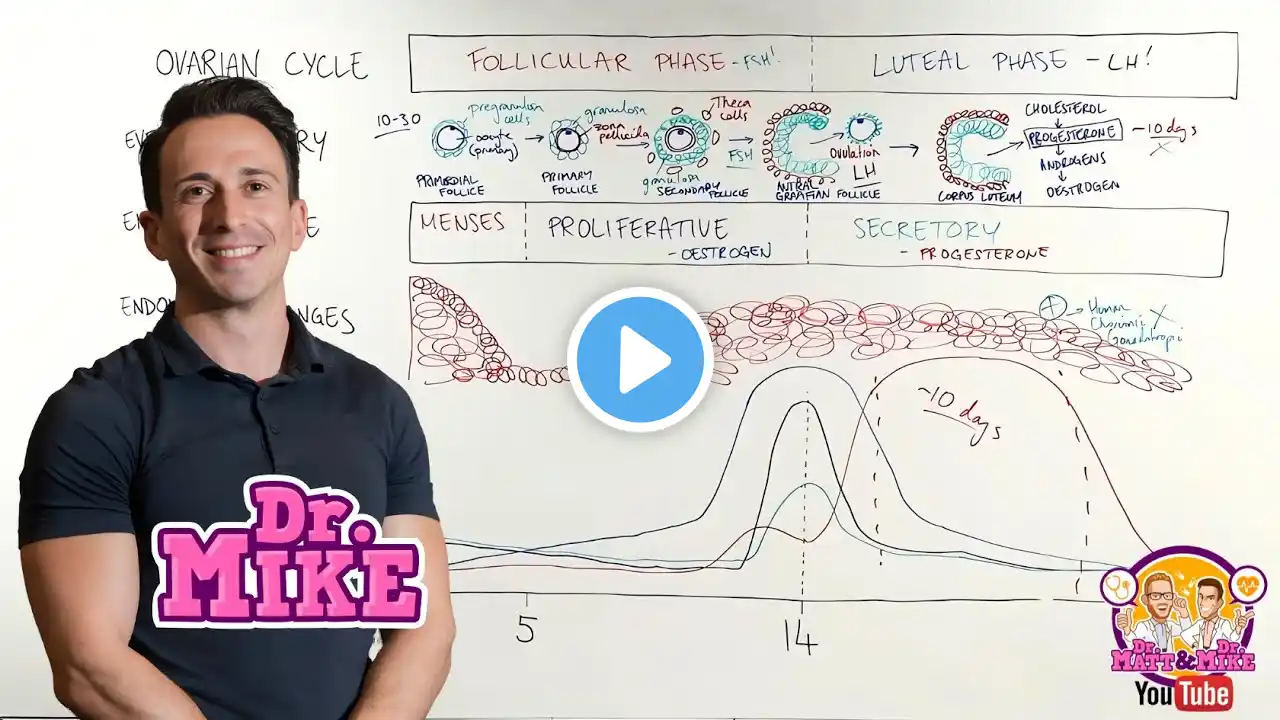
Menstrual cycle explained: includes hormone phases in a woman explained (of the female reproductive system). These phases include the ovarian phases: Follicular, Ovulation, and Luteal and the uterine phases: Menstrual, Proliferative, and Secretory. A typical menstrual cycle in a woman is 28 days. The follicular phase of the ovarian cycle is approximately 1-13 cycle days and occurs simultaneously as the menstrual and proliferative phase of the uterine cycle. The menstrual phase occurs cycle days 1-6, while the proliferative phase occurs cycle days 7-14. During the menstrual phase, the stratum functionalis layer of the endometrium is shed. This phase occurs during the follicular phase. During the follicular phase the hypothalamus is releasing gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) which stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release follicular-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). FSH stimulates the follicles in the ovary to mature. One follicle will mature into what is called a Graafian follilce which will release a mature egg called an ovum. As the follicle matures it steadily releases estrogen which causes the uterus to rebuild the stratum functionalis layer of the endometrium (during the proliferative phase) for possible implantation of a fertilized ovum. Once the Graafian follicle is mature estrogen peaks to a point where it will cause a positive feedback loop to the anterior pituitary gland which will cause a massive amount of luteinzing hormone to be release (known as the LH surge). LH causes the wall of the graafian follicle to break down and helps release the egg. Luteinizing hormone also turns the follicle into the corpus luteum. 24-36 hours after the LH surge ovulation occurs. Ovulation tends to occur on cycle day 14. Next is the luteal and secretory phase which occurs simultaneously as well. During the luteal phase, the corpus luteum is formed which releases progesterone and estrogen. These hormones play a role in making the endometrium ready for possible implantation. If pregnancy does not occur the corpus luteum will die in 14 days and turn in the corpus albicans and progestrone and estrogen levels will drop. This will signal for the hypothalamus to release GnRH which cause the anterior pituitary gland to release FSH and LH causing the reproductive cycle to start all over again. If fertilization of the ovum occurs, the fertilized egg will release HcG. HcG will prevent the corpus luteum from dying so pregnancy can be maintained. Once the placenta is fully developed it will take over with the secretion of progesterone and estrogen (which will occurs around 8 weeks gestation) and then the corpus luteum will die. Quiz on Menstrual Cycle: https://www.registerednursern.com/men... Lecture Notes: https://www.registerednursern.com/men... More Maternity Nursing Lectures: • Maternity Nursing Lectures Subscribe: http://www.youtube.com/subscription_c... Nursing School Supplies: http://www.registerednursern.com/the-... Nursing Job Search: http://www.registerednursern.com/nurs... Visit our website RegisteredNurseRN.com for free quizzes, nursing care plans, salary information, job search, and much more: http://www.registerednursern.com Check out other Videos: / registerednursern Popular Playlists: NCLEX Reviews: • NCLEX Study Strategies Fluid & Electrolytes: • Fluid and Electrolytes Nursing Nursing Skills: • Nursing Skills Videos Nursing School Study Tips: • Nursing School Study Tips Nursing School Tips & Questions" • Nursing School Tips & Questions Teaching Tutorials: • Teaching Tutorials Types of Nursing Specialties: • Types of Nursing Specialties Healthcare Salary Information: • Healthcare Salary Information New Nurse Tips: • New Nurse Tips Nursing Career Help: • Nursing Career Help EKG Teaching Tutorials: • EKG/ECG Interpretation Personality Types: • Playlist Dosage & Calculations for Nurses: • Dosage Calculations Nursing Diabetes Health Managment: • Diabetes Health Managment