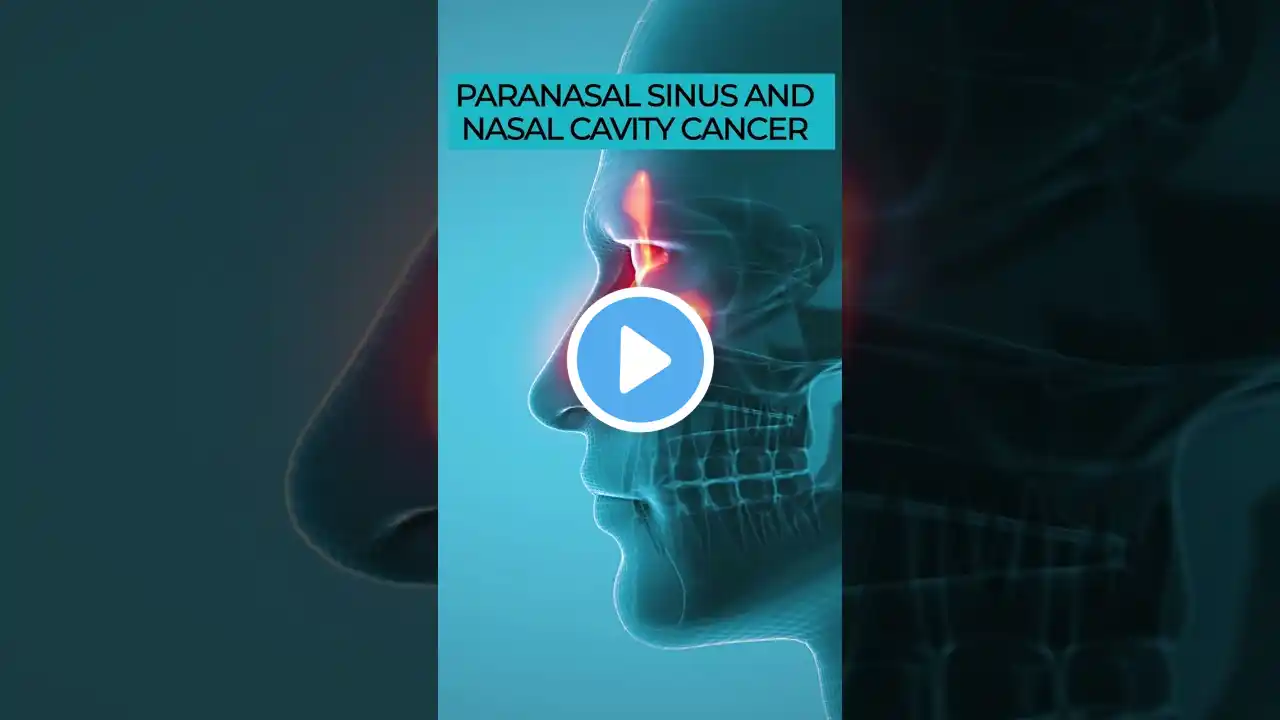
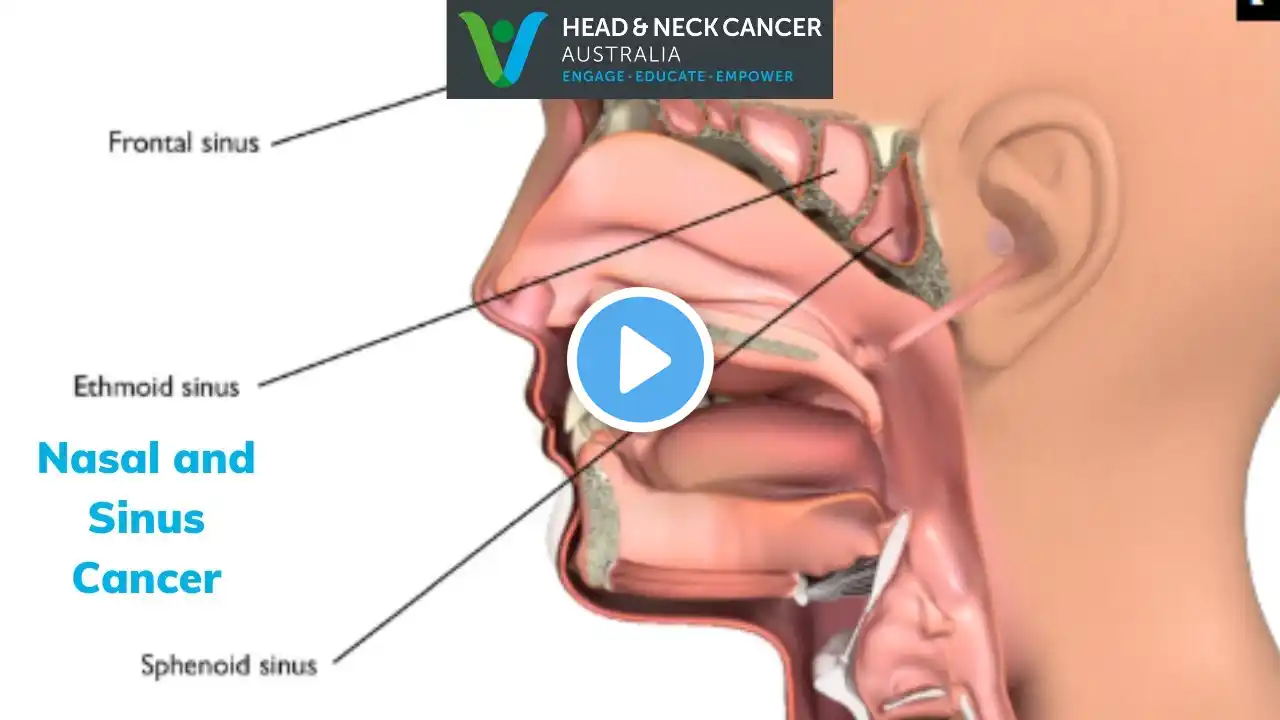
Maxillary Sinus Cancer Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments Explained
Medical Centric Recommended : (Affiliate Links) Thermometer ➝ https://amzn.to/3Yy5aGL Blood pressure machine ➝ https://amzn.to/3CnhgLl Bandage wrap or medical tape ➝ https://amzn.to/4hyVa8N Gauze rolls ➝ https://amzn.to/3UzCdci Sanitizer ➝ https://amzn.to/3AoBxjg Alcohol prep pads ➝https://amzn.to/3UvEMfl Breast pump ➝ https://amzn.to/40zVQEX Toilet seats with handle ➝ https://amzn.to/3CnigPB Walker/ handicap scooters ➝ https://amzn.to/3UCI8NX Sticks ➝ https://amzn.to/40wtfjP Weight machine ➝ https://amzn.to/3YA43WX Ice packs ➝ https://amzn.to/4ehuarH Splint ➝ https://amzn.to/3AtRODr Waterproof bed pads ➝ https://amzn.to/3NROCVf Stethescope ➝ https://amzn.to/3YNTP6R Pill organizer ➝ https://amzn.to/3UzDsIu Massage chair or massage related products ➝ https://amzn.to/3UChfcW Compression socks ➝ https://amzn.to/4edl2V0 Knee brace/stabilizers ➝ https://amzn.to/4fymF0n ______________________________________________________________ Maxillary Sinus Cancer Symptoms, Causes, and Treatments Explained Here's a draft of the English text: Maxillary Sinus Cancer: Everything You Should Know Maxillary sinus cancer is a relatively rare type of cancer that develops in the maxillary sinuses, located in the cheekbones. These sinuses are part of the paranasal sinus system, which helps to humidify air and produce mucus to trap dust and allergens. This blog post delves into the essential details of maxillary sinus cancer, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options. What is Maxillary Sinus Cancer? Maxillary sinus cancer occurs when malignant cells develop in the lining of the maxillary sinuses. The most common type is squamous cell carcinoma, although other forms, such as adenocarcinoma or lymphoma, can also occur. Symptoms to Watch For The symptoms of maxillary sinus cancer often mimic less severe sinus issues, making early detection challenging. Key symptoms include: Persistent nasal congestion or blockage (usually on one side) Frequent nosebleeds or unusual nasal discharge Swelling or pain around the cheek, upper jaw, or teeth Numbness in the face A lump or mass in the cheek or roof of the mouth Blurred vision or double vision in advanced cases If these symptoms persist or worsen, seek medical attention promptly. Causes and Risk Factors While the exact cause isn't always clear, several risk factors are associated with maxillary sinus cancer: Exposure to Carcinogens: Prolonged exposure to wood dust, leather dust, and certain chemicals in the workplace. Smoking: Tobacco use significantly increases the risk. Human Papillomavirus (HPV): Certain strains of HPV are linked to sinus cancers. Chronic Sinusitis: Long-term inflammation might play a role in some cases. Diagnosis Early diagnosis can significantly improve outcomes. Common diagnostic tools include: Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, or PET scans to locate and assess the tumor. Nasal Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera examines the nasal cavity. Biopsy: A tissue sample confirms the presence of cancer cells. Blood Tests: Rule out other conditions and check for general health. Treatment Options Treatment depends on the stage and type of cancer. Common approaches include: Surgery: Often the first line of treatment, it involves removing the tumor and, in some cases, affected surrounding tissues. Radiation Therapy: High-energy beams target and kill cancer cells post-surgery or in cases where surgery isn't possible. Chemotherapy: Used alongside radiation or for advanced stages to shrink or slow tumor growth. Targeted Therapy: Focuses on specific genetic changes in cancer cells to limit growth with fewer side effects. Prognosis and Prevention The prognosis depends on the cancer's stage at diagnosis and the individual's overall health. Early-stage cancers have higher survival rates, emphasizing the importance of early detection. Preventive measures include avoiding known carcinogens, quitting smoking, and addressing persistent sinus issues with a healthcare provider. Conclusion Maxillary sinus cancer is rare but treatable, especially if detected early. Awareness of symptoms and risk factors can lead to timely intervention, potentially improving outcomes. If you experience persistent sinus issues or notice unusual symptoms, consult an ENT specialist without delay. Early action saves lives!