Anemia || introduction ||Classification In हिंदी Essy way to learning Anemia
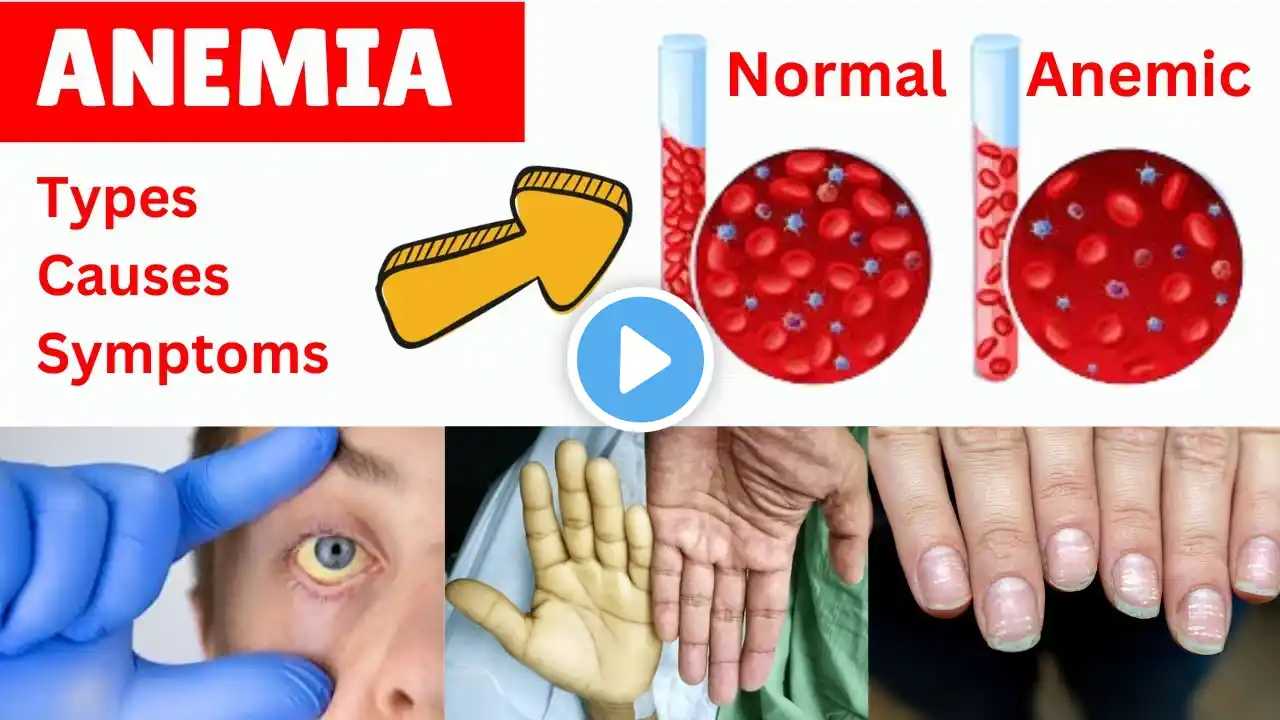
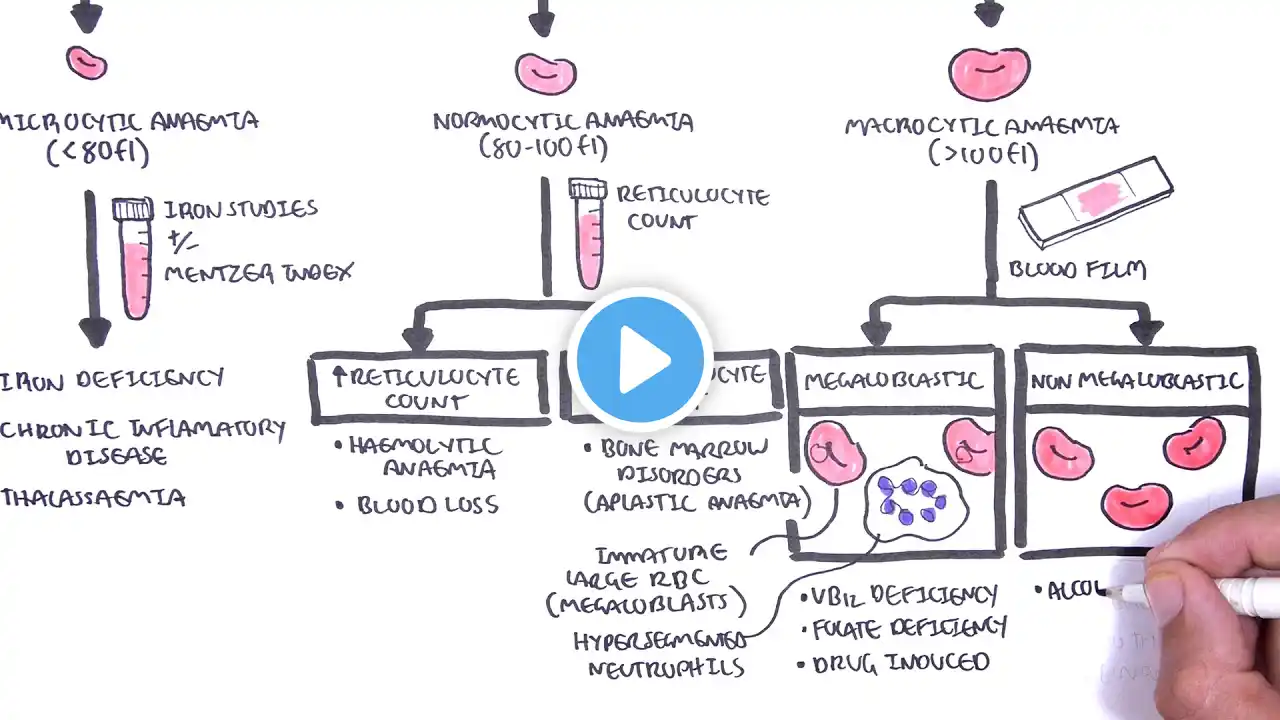
#anemia #anemia_classification_in_hindi #anemia_introduction_in_hindi #anemia_in_hindi #anemia_notes #anemia_lab_diagnosis #dr_najeeb #anemia_treatment #anemia_symptoms Best book for microbiology. https://www.flipkart.com/text-practic... Question ? Definative of anemia Introduction of anemia Classification of anemia Morphological classification of anemia Normocytic Anemia Microcytic Anemia Macrocytic anemia What is hemoglobin Functions of hemoglobin Types of hemoglobin Normal range of RBC Normal range of Hemoglobin Anemia for nursing Role of hemoglobin in O2 transport (Hb/O2 dissociation curve): Anemia for DMLT and BMLT Anemia Classification Sample EDTA blood is needed. For RBC morphology, a direct smear is preferred.` Bone marrow is also advised. Also, a bone biopsy may be needed. Definition Of Anemia Anemia is defined as a decrease in hemoglobin concentration depending upon the patient’s age and sex. The diagnostic criteria are low hemoglobin, low hematocrit (Hct), or decreased RBC count. Criteria for the anemia: Effective erythropoiesis depends upon: Level of iron and cobalt. Vitamin B12. Vitamin B6. Riboflavin. Thiamine. Vitamin C. Vitamin E. Hormones like: Androgens. Thyroxine. Hemoglobin facts: To understand the anemias, it is better to know the hemoglobin types and structure: Hemoglobin functions: RBCs in arterial blood carry O2 from the lungs to the tissue and take back CO2 in the venous blood Anemia classification: Anemia may be classified roughly based on Hb level: Severe anemia when the Hb is 7 g/dL. Moderate when the Hb is This group will not produce evident S/S. in most of the cases. Anemia classification based on RBC morphology: Normochromic and normocytic anemias are due to: Anemia of acute hemorrhage. Hemolytic anemia. Anemia due to chronic diseases. Hypochromic and microcytic anemias are due to: Iron deficiency anemia. Thalassemia. Normochromic and macrocytic anemias are due to: Vit. B12 deficiency. Folate deficiency. Anemia classification based on physiological abnormality: Defective maturation of erythropoiesis. Hemolytic anemia where is the increased breakdown of the RBCs. Defect due to an increase in RBC precursors compared to the degree of anemia. Anemia classification based on etiology: Increased RBCs destruction due to intra or extra red blood cell defects. Increased blood loss, which may be acute or chronic. Defective RBCs formation due to Lake of factors necessary for erythropoiesis. Anemia classification based on etiology: Increased RBCs destruction due to intra or extra red blood cell defects. Increased blood loss, which may be acute or chronic. Defective RBCs formation due to Lake of factors necessary for erythropoiesis. Anemia classification based on the category: increased destruction of the RBCs Hemolytic anemia (nonimmune). Immune hemolytic anemia. Anemia due to blood loss in hemorrhage. Nutritional deficiency like folate or vitamin B12 deficiency. Toxicity due to drugs. Infections. Infiltration of the bone marrow by the cancer cells. Hereditary or acquired defect in the RBCs. Hematopoietic stem cell arrest or damage. Idiopathic or unknown cause. Anemia classification based on RBC indices: Signs and symptoms of the anemias: Clinically S/S seen are: The main symptoms are due to cardiovascular system adaptation. There are increased stroke volume, tachycardia, and the Hb O2 dissociation curve changes. Hyperdynamic circulation leads to tachycardia, a bounding pulse, systolic murmurs, especially at the apex, and cardiomegaly. Older adults may find S/S of congestive heart failure. In Acute onset effect: There is an effect on the speed of onset; acute onset has more S/S compared to the slow onset. The severity of the anemia: In the case of mild anemia, there is no S/S. Types of Anemias Anemia is divided based on RBCs indices (MCV) into the following categories: The causes of normochromic and normocytic anemia are: Iron deficiency in the early stages. Acute blood loss. Chronic diseases of the kidneys and the liver. Infiltration by leukemia and multiple myeloma. Drugs like chloramphenicol cause aplastic anemia. Acquired hemolytic anemia may be from the prosthetic surgery of the heart. Pregnancy due to increased plasma volume. Overhydration. DMLT MCQ book https://www.flipkart.com/lab-tecnicia... Best camera for video and photo Canon EOS 15000D https://www.flipkart.com/canon-eos-15...