Laws Of Motion | Static Friction And Kinetic Friction, NLM CLASS 11, NLM #yt #nlm #physics #friction
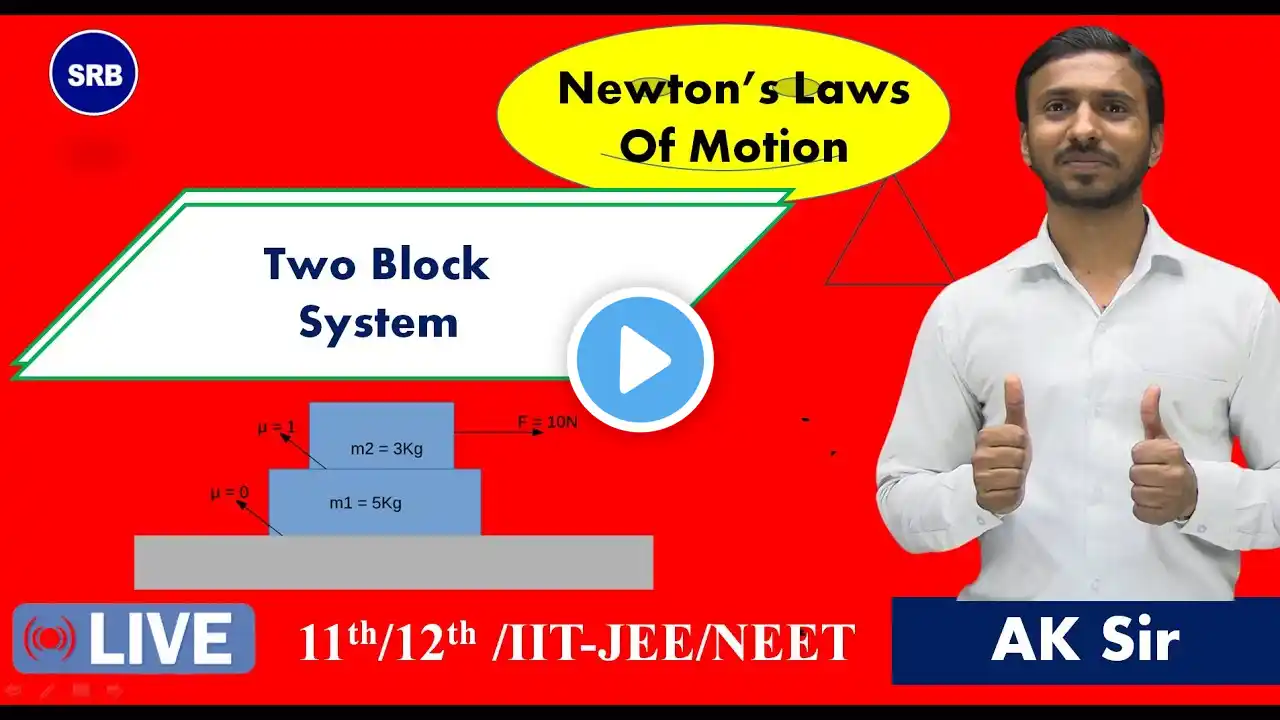
Laws Of Motion | Static Friction And Kinetic Friction, NLM CLASS 11, NLM #yt #nlm #physics #friction In today's live session, In the first law, an object will not change its motion unless a force acts on it. In the second law, the force on an object is equal to its mass times its acceleration. In the third law, when two objects interact, they apply forces to each other of equal magnitude and opposite direction. Newton's laws of motion are three laws that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. न्यूटन का प्रथम नियम: यदि कोई वस्तु गतिमान है तो वो गतिमान ही रहेगी और अगर कोई वस्तु स्थिर है तो वो स्थिर ही रहेगी जब तक की उस पर कोई वाह्य बल न लगे | न्यूटन के गति नियम भौतिक नियम हैं जो चिरसम्मत यांत्रिकी के आधार हैं। यह नियम किसी वस्तु पर लगने वाले बल और उससे उत्पन्न उस वस्तु की गति के बीच सम्बन्ध बताते हैं। Newtons laws of motion solution and explanation(discussion). In NLM by using free body diagram anyone can solve easily question. Newtons second law is rate of change of momentum with respect to time is called force(net force). Newtons third law is action reaction law, every action has equal and opposite reaction. A pseudo force, also called a fictitious force or an inertial force, is an apparent force that acts on all bodies whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of reference, such as a rotating reference frame. A pseudo force arises when a frame of reference is accelerating compared to a non-accelerating frame. A fictitious force is a force that appears to act on a mass whose motion is described using a non-inertial frame of reference, such as a linearly accelerating or rotating reference frame. Here, we will look at some problems based on the pulley and learn how to solve them. Know about Free Body Diagrams (FBD), the tension in strings, etc. Static friction is the force of friction on an object that is not moving. If you push on a stationary block and it doesn't move, it is being held by static friction which is equal and opposite to your push. Kinetic friction is a force that acts between moving surfaces. An object that is being moved over a surface will experience a force in the opposite direction as its movement. The magnitude of the force depends on the coefficient of kinetic friction between the two kinds of material. Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. Types of friction include dry, fluid, lubricated, skin, and internal. JEE Mains PYQs 2022 & 2023 Playlists Topicwise • Physics JEE Mains PYQs 2023 JEE Mains 2024 Questions Paper Discussion • JEE Mains 2024 Questions #newton #newtonslawofmotion #newtonslawsofmotion #jeemain2024 #jeemain2025 #jeemainsphysics #jeemainspyq #jeemainspyqs #physics11 #physicspyq #newtonslaw #srbphysicskota #aksirphysics #aksir jee, jee 2024, jee exam, jee exam 2024, jee main, jee advanced, laws of motion, laws of motion jee, laws of motion jee main, laws of motion jee advanced, laws of motion one shot, laws of motion jee one shot, laws of motion physics, laws of motion physics Class 11th, laws of motion physics class 11, laws of motion class 11 jee main, laws of motion most important questions jee, laws of motion class 11, static friction, static friction class 11th, static friction class 11, static friction 11th, kinetic friction, kinetic friction class 11th, kinetic friction class 11, kinetic friction 11th, friction, friction class 11th, friction class 11, friction physics,