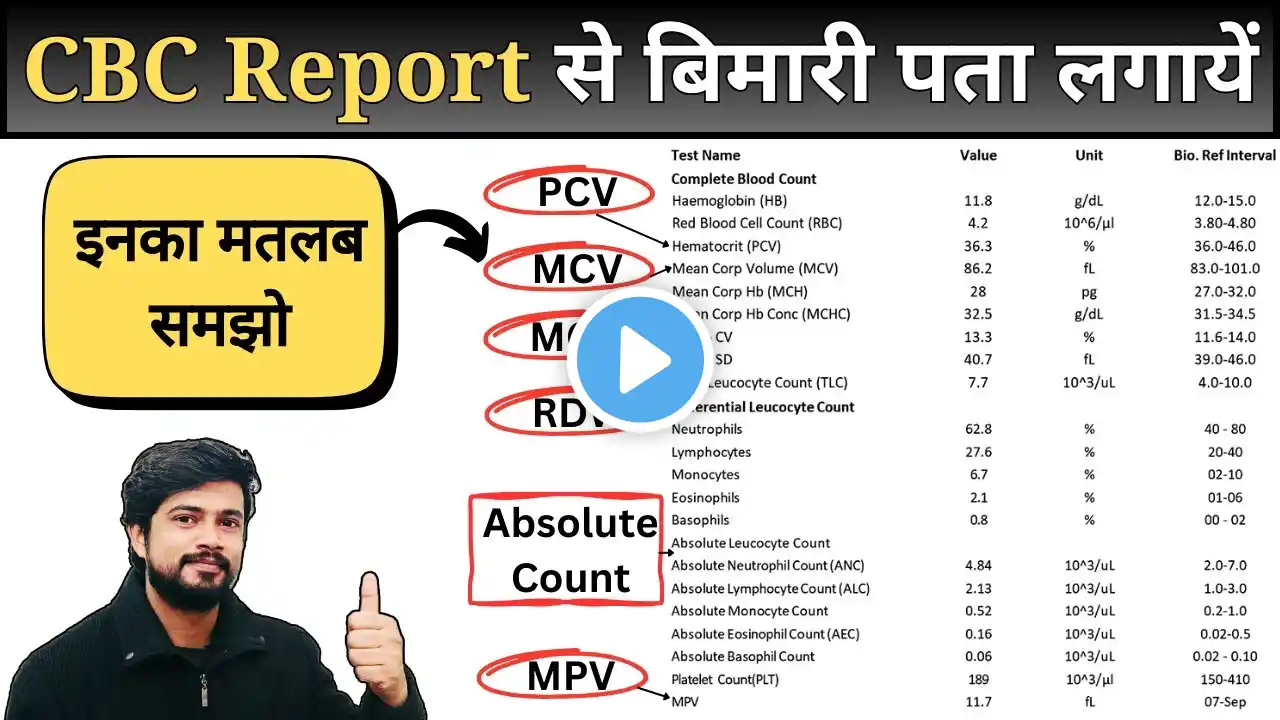
2. Diseases of Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Hindi: Pathology Lectures
𝐒𝐮𝐛𝐬𝐜𝐫𝐢𝐛𝐞 𝗙𝐨𝐫 𝗠𝐨𝐫𝐞 𝗜𝐧𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦𝐚𝐭𝐢𝐨𝐧 𝐨𝐧 𝗛𝐞𝐚𝐥𝐭𝐡 👩⚕ 𝐚𝐧𝐝 𝗠𝐞𝐝𝐢𝐜𝐢𝐧𝐞💉🩺💊 📌𝗜𝗻𝘀𝘁𝗮𝗴𝗿𝗮𝗺 : / clinical.learning Diseases of Red Blood Cells (RBCs) - -------------------------------------------------------------- Red Blood Cell (RBC) disorders primarily affect their production, structure, or function, leading to various clinical conditions. The most common diseases include anemia, characterized by reduced RBC count or hemoglobin, resulting in fatigue, pallor, and dyspnea. Iron-deficiency anemia is the most prevalent type, caused by inadequate iron, often due to malnutrition, chronic blood loss, or increased demand (e.g., pregnancy). Megaloblastic anemia, caused by vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency, leads to the production of large, immature RBCs. Hemolytic anemias, such as sickle cell disease and thalassemia, result from premature RBC destruction due to abnormal hemoglobin or structural defects. Aplastic anemia involves bone marrow failure, reducing RBC production. Polycythemia, the opposite of anemia, involves excessive RBCs, increasing blood viscosity and risk of thrombosis. These disorders disrupt oxygen delivery, impairing cellular metabolism. Diagnosis involves complete blood count (CBC), peripheral smear, and bone marrow studies. Management varies from nutritional supplementation to advanced therapies like blood transfusions or bone marrow transplantation, depending on the underlying cause. Understanding RBC pathologies is critical for addressing systemic effects and improving patient outcomes. 🩸✨💉 #RBCDisorders #AnemiaExplained #HematologyBasics #BloodHealth #MedicalEducation #MBBSNotes #StudySmart