(NSAIDS) Mechanism of Action | Adverse Effects | NSAIDS PHARMACOLOGY
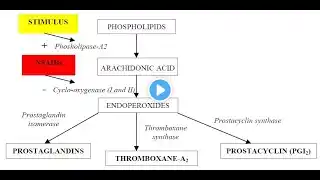
NSAIDS PHARMACOLOGY Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are a class of medications that work by inhibiting the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), thereby reducing inflammation, pain, and fever. They are commonly used to treat conditions such as arthritis, headaches, and menstrual cramps. Examples include ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen. However, prolonged use or high doses can lead to adverse effects like gastrointestinal ulcers, kidney problems, and increased risk of cardiovascular events. NSAIDS MECHANISM OF ACTION The mechanism of action of NSAIDs involves inhibition of the enzyme cyclooxygenase (COX), which plays a crucial role in the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid. Prostaglandins are lipid compounds that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever. By inhibiting COX, NSAIDs reduce the production of prostaglandins, thereby decreasing inflammation, relieving pain, and lowering fever. There are two isoforms of COX: COX-1 and COX-2. Traditional NSAIDs inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2, while selective COX-2 inhibitors target only COX-2, potentially reducing some adverse effects associated with COX-1 inhibition, such as gastrointestinal ulcers. Uses NSAIDS Uses,adverse effects and side effects Uses: Pain Relief: NSAIDs are commonly used to relieve pain, including headaches, menstrual cramps, dental pain, and musculoskeletal pain. Anti-inflammatory: They reduce inflammation, making them effective for conditions like arthritis, tendonitis, and bursitis. Fever Reduction: NSAIDs can lower fever by acting on the hypothalamus, the body's temperature-regulating center. Adverse Effects: Gastrointestinal Effects: NSAIDs can irritate the stomach lining, leading to gastritis, ulcers, or even gastrointestinal bleeding. Renal Effects: Prolonged use of NSAIDs can cause kidney damage, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions or those who are dehydrated. Cardiovascular Effects: NSAIDs, especially at high doses or in people with cardiovascular risk factors, may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. Hepatic Effects: Rarely, NSAIDs can cause liver damage, although this is more common with certain NSAIDs like diclofenac. Hematologic Effects: NSAIDs can interfere with platelet function, increasing the risk of bleeding, particularly when combined with other blood-thinning medications. Side Effects: Nausea and Dyspepsia: Common gastrointestinal side effects include nausea, indigestion, and stomach pain. Dizziness and Headache: Some people may experience dizziness or headache as a side effect of NSAIDs. Allergic Reactions: Rarely, NSAIDs can cause allergic reactions ranging from mild skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis. Fluid Retention: NSAIDs may cause fluid retention and edema, particularly in individuals with heart failure or kidney disease. High Blood Pressure: Long-term use of NSAIDs can elevate blood pressure, which may be problematic for individuals with hypertension. It's essential to use NSAIDs cautiously and under medical supervision, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or those taking other medications. Always follow the recommended dosage and duration of use to minimize the risk of adverse effects. QURIES SOLVED 1 NSAIDS INTRODUCTION 2 MECHANISM OF ACTION 3 ADVERSE EFFECTS 4 SIDE EFFECTS 5 USES OF DRUGS Thanks PHYSIO FIELD ACADEMY Avoid tags nsaids mechanism of action, nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, pharmacology of nsaids, pharmacology, cox, cyclooxygenase enzymes, cyclooxygenase pathway, nsaids mechanism of action animation, nsaids pharmacology nursing, nsaids, anti-inflammatories, antiinflammatory, prostaglandins, antipyretic, analgesic, pgs, pain medications, cox-1 vs cox-2, non-selective nsaids, aspirin, anti-thrombotic, cox inhibitors, cytoprotection, peptic ulcer disease, cox-2-specific Instagram account https://www.instagram.com/shailab_sag... Telegram PHYSIO FIELD ACEDMY Explore a world of wellness on our physiotherapy channel! Dive into expert-guided exercises https://t.me/pfaphysiotherapy