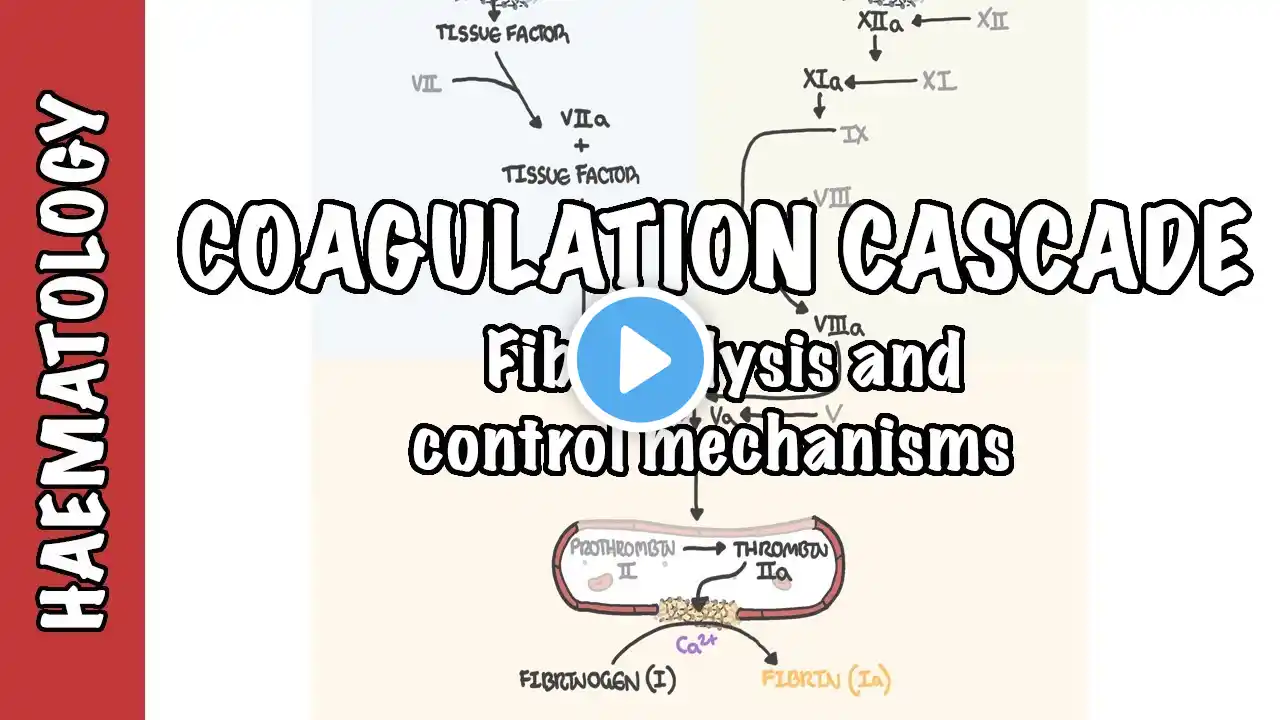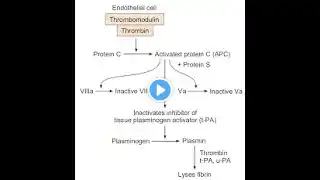
Protein S and C As Negative Feedback inhibitor of Blood Coagulation Pathway
Protein S and Protein C are essential components of the body's natural anticoagulant system, acting as negative feedback inhibitors of the blood coagulation pathway. Protein S Role: Protein S serves as a cofactor for activated Protein C (APC). It enhances the activity of APC in inactivating Factors Va and VIIIa, which are crucial for the propagation of blood clotting1. Mechanism: By inhibiting these factors, Protein S helps to limit the formation of thrombin and prevent excessive clot formation. Protein C Role: Protein C is a vitamin K-dependent protein that, when activated to APC, plays a significant role in regulating blood coagulation. Activation: Protein C is activated by forming a complex with thrombin and thrombomodulin on the surface of endothelial cells. Mechanism: Activated Protein C (APC) inactivates Factors Va and VIIIa, reducing thrombin generation and promoting fibrinolysis (clot breakdown). Together, Protein S and Protein C work to maintain a delicate balance in the coagulation system, preventing both excessive clotting and bleeding #NegativeFeedback