Intracranial Aneurysm or Cerebral Aneurysm or Brain Aneurysm ; Definition, causes, Symptoms, Diagnos
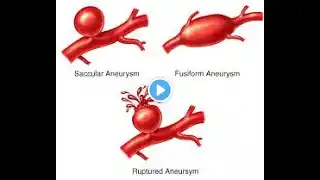
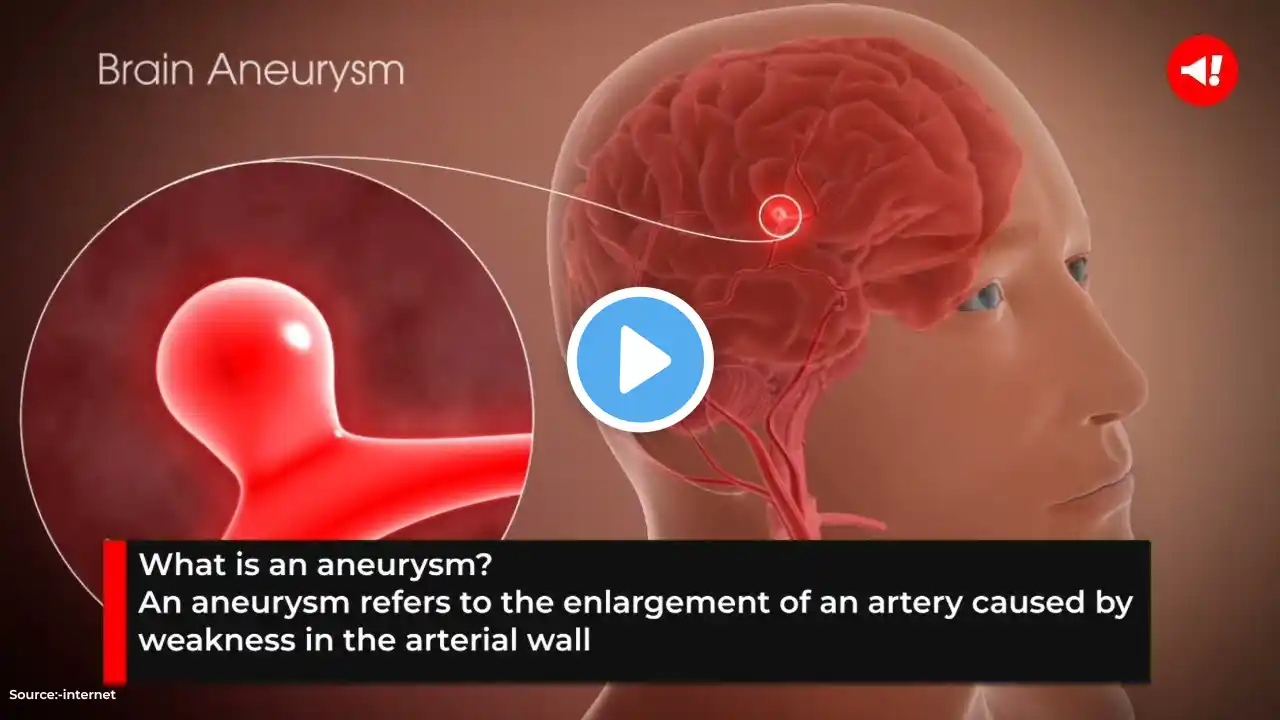
An intracranial aneurysm, also known as a brain aneurysm or cerebral aneurysm, is a bulge or ballooning in a blood vessel in the brain. Here are some key points: Characteristics Location: Most commonly found in the arteries at the base of the brain, known as the Circle of Willis. Types: There are different types of aneurysms, including saccular (berry) aneurysms and fusiform aneurysms. Size: Aneurysms can vary in size from small to giant, with larger aneurysms having a higher risk of rupture. Symptoms Unruptured Aneurysm: Often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally during imaging for other conditions. Ruptured Aneurysm: Can cause a sudden, severe headache (often described as the worst headache ever), nausea, vomiting, vision problems, and loss of consciousness3. Causes and Risk Factors Hypertension: High blood pressure is a significant risk factor. Genetic Factors: Family history of aneurysms, certain genetic conditions like polycystic kidney disease. Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug abuse (e.g., cocaine), and head trauma. Infections: Infections can weaken the arterial walls and contribute to aneurysm formation. Diagnosis Imaging: CT scans, MRI, and angiography are used to detect and assess the size and location of aneurysms. Lumbar Puncture: In cases of suspected subarachnoid hemorrhage, a lumbar puncture may be performed to detect blood in the cerebrospinal fluid. Treatment Observation: Small, asymptomatic aneurysms may be monitored regularly. Surgical Clipping: A surgical procedure to place a clip at the base of the aneurysm to prevent blood flow into it. Endovascular Coiling: A less invasive procedure where coils are placed within the aneurysm to promote clotting and prevent rupture. Pipeline Embolization: A newer technique used for larger or complex aneurysms. Prognosis Ruptured Aneurysm: Requires immediate medical attention and can be life-threatening. The prognosis depends on the size, location, and speed of treatment2. Unruptured Aneurysm: Generally has a better prognosis, especially if detected early and monitored regularly. Would you like more detailed information on any specific aspect of intracranial aneurysms? #Aneurysm